前言
动机
最近在学习Netty框架,发现Netty是支持Http协议的。加上以前看过Spring-MVC的源码,就想着二者能不能结合一下,整一个简易的web框架(PS:其实不是整,是抄)
效果
项目地址:terabithia
0.3版本使用效果如下,其实就是Spring-MVC的Controller的写法
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public class HelloController {
/**
* request url:/hello/testGet?strParam=test&intParam=1&floatParam=2&doubleParam=3
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testGet", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public Object testGet(ParamWrapperRequest request, String strParam, Integer intParam, Float floatParam, Double doubleParam) throws Exception{
System.out.println(request.getParameterNames());
// 获取参数
System.out.println("strParam:" + strParam);
System.out.println("intParam:" + intParam);
System.out.println("floatParam:" + floatParam);
System.out.println("doubleParam:" + doubleParam);
System.out.println("testGet");
return request.getParameterMap();
}
}
前置条件
以下列出各个版本需要掌握的知识:
- 0.1版本:Netty
- 0.2版本:Netty
- 0.3版本:Netty + Spring-MVC
0.1版本
0.1版本就是Netty原生API对Http协议的支持
如何实现
HttpServer初始化Netty服务,HttpServerCodec和HttpObjectAggregator提供了对Http的支持,HttpServerHandler处理业务逻辑。
public class HttpServer {
private static final int PORT = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) {
final EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
final EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
final ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
// 临时存放已完成三次握手的请求的队列
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new HttpServerCodec())
//把多个消息转换为一个单一的FullHttpRequest或是FullHttpResponse
.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536))
.addLast(new HttpServerHandler());
}
});
final Channel ch = b.bind(PORT).sync().channel();
ch.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
public class HttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
// 业务逻辑处理。。。
String result = "hello world";
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK);
response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8");
response.content().writeBytes(result.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, response.content().readableBytes());
response.headers().set(CONNECTION, CLOSE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
局限性
无法专注于业务处理,HttpServerHandler需要处理Netty的API和业务逻辑
0.2版本
0.1版本在同一个Handler中处理业务和网络是不合适的,想办法将HttpServerHandler解耦, 划分Handler和Controller。Handler处理Netty API,Controller处理业务逻辑。
如何实现
此版本不讲代码,讲思路(PS:主要是我懒得写)
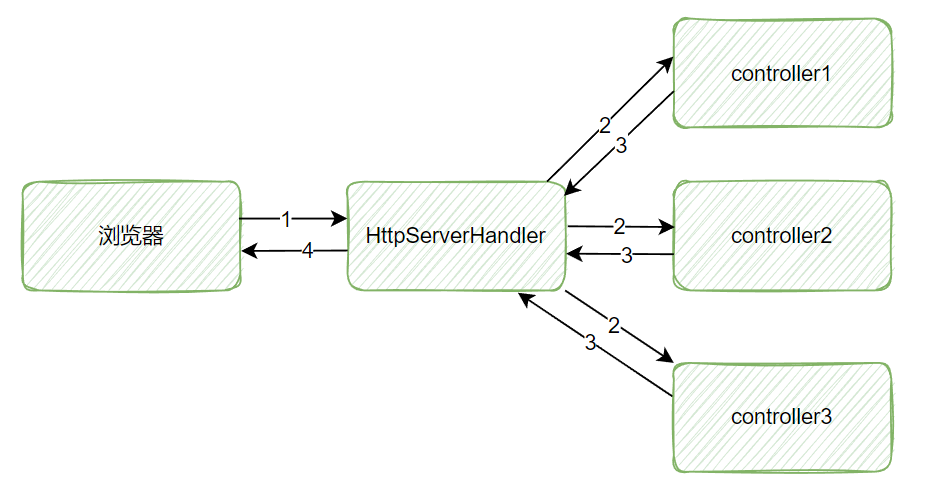
- HttpServerHandler处理Netty API,转发请求到Controller以及处理Controller的返回值
- 获取请求uri,根据uri找到相对应的Controller以及方法
- 调用Controller的方法
- 处理Controller的返回值,封装成HttpResponse返回
- Controller处理业务逻辑,怎么在Spring-MVC用Controller,在这里就怎么用
Controller的主要问题是如何根据uri找到相对应的Controller以及方法,下面给出两种思路:
- 自定义接口方式,并有Map存放uri与Controller的关系
// 表示是Controller的接口 public interface Action { Object doAction(FullHttpRequest request); } // 业务Controller public class HelloAction implements Action{ @Override public Object doAction(FullHttpRequest request) { // 业务逻辑处理 return null; } } // 使用Map存放uri与Controller的关系 Map<String, Action> actionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); actionMap.put("/hello", new HelloAction()); // 而在HttpServerHandler调用就更简单了,不用反射 actionMap.get(uri).doAction(request); - 自定义注解方式
// 表示是Controller的注解 @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface RequestMapping { String value() default ""; } // 业务Controller @RequestMapping("/hello") public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/index") public FullHttpResponse index(FullHttpRequest request) { return null; } } // // 而在HttpServerHandler调用 // Class<?> clazz = obj.getClass(); // 获取类上的注解 RequestMapping mapping = clazz.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class); if (mapping != null) { String mappingUri = mapping.value(); // 获取controller的所有方法 for (Method actionMethod : clazz.getMethods()) { // 获取方法上的注解 RequestMapping subMapping = actionMethod.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class); if (subMapping != null) { String subMappingUri = subMapping.value(); // 如果uri符合注解规则,则反射调用方法 if (uri.equalsIgnoreCase(mappingUri + subMappingUri)) { return (FullHttpResponse) actionMethod.invoke(obj, request); } } } }
- 自定义接口方式,并有Map存放uri与Controller的关系
局限性
没有一般web框架的过滤器,参数处理,返回值处理等。业务代码仍然深度依赖Netty API
0.3版本
结构
依赖:Netty + SpringBoot
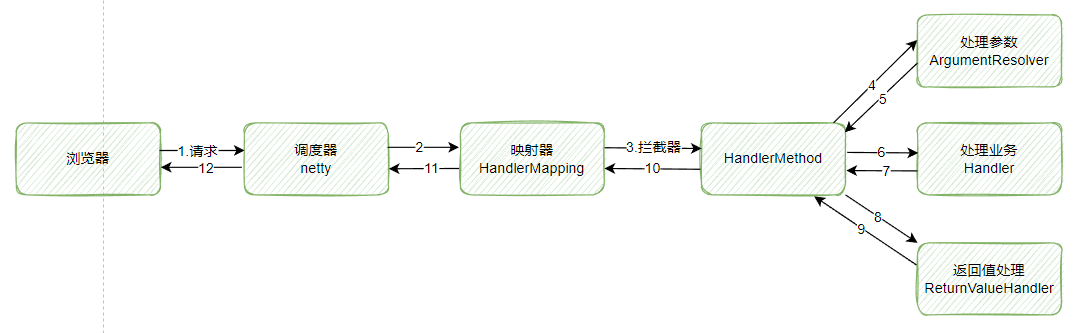
处理流程图如下:
思路
下文说的Handler就是Controller
- 先说说为什么依赖SpringBoot,因为代码抄的是Spring-MVC的,而且SpringBoot提供的容器API真的很方便。
- 调度器:作为一个业务框架,需要业务逻辑对底层的依赖,也就是要满足大部分业务处理不会用到Netty的API,也就是Netty专注于接收和响应HTTP请求
- HandlerMapping:存储了请求路径与HandlerMethod的关系,可以通过uri定位到对应的Controller的方法
- HandlerMethod:存储了Controller和业务处理方法的信息
- ArgumentResolver:负责将请求参数转换成业务处理方法所需的参数(PS:Spring的DataBinder是个好东西)
- ReturnValueHandler:负责返回值的转换,比如将Map转成JSON
实现
实现有太多东西讲了,文章讲不完。我抄了一个简化版的Spring-MVC,就在文章开头的项目地址,感兴趣的自行去看吧。